netosis|netosis cell death : Tuguegarao NET activation and release, or NETosis, is a dynamic process that can come in two forms, suicidal and vital NETosis. Overall, many of the key components of the process are similar for both types of NETosis, however, there are key differences in stimuli, timing, and ultimate result. The full NETosis activation pathway is still under investigation but a few key proteins have been identified and slowly a full picture of the pathway is emerging. The process is thought to begin with WEBJogo - Anatomia do Sistema Nervoso Central. Quiz Online. acessar o jogo. Jogo - Anatomia do Neurônio. Quiz Online. acessar o jogo. Jogo - Placa Motora. Quiz Online. acessar o jogo. Jogo - Áreas do Telencéfalo. Quiz Online. acessar o jogo. Jogo - Tipos de Músculos do Corpo. Quiz Online. acessar o jogo.
0 · netosis全称
1 · netosis pma
2 · netosis meaning
3 · netosis cell death
4 · netosis cancer
5 · netosis bacterial killing
6 · netosis assay kit
7 · netosis assay
8 · More
26 de out. de 2023 · Acumulado para Sorteio. Especial Mega da Virada: R$ 93.389.945,23. Acumulado. próximo concurso: R$ 78.338.906,99. O prêmio da Mega Sena previsto .
netosis*******NETosis is a program for formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), which consist of modified chromatin decorated with bactericidal proteins from granules and cytoplasm. Various pathogens, antibodies and immune complexes, cytokines, .
In this review, we examine the evidence that neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) play a critical role in innate immunity. We .NET activation and release, or NETosis, is a dynamic process that can come in two forms, suicidal and vital NETosis. Overall, many of the key components of the process are similar for both types of NETosis, however, there are key differences in stimuli, timing, and ultimate result. The full NETosis activation pathway is still under investigation but a few key proteins have been identified and slowly a full picture of the pathway is emerging. The process is thought to begin with NETosis is a regulated form of neutrophil cell death that contributes to the host defense against pathogens and was linked to various diseases soon after its first .netosis netosis cell death Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) cause pathology in a number of conditions through several mechanisms. Direct cell damage is implicated in infection, sepsis, autoimmunity and diabetes. By .
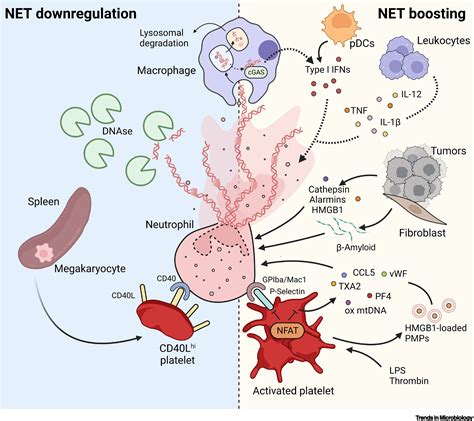
NETs are weblike DNA structures decorated with histones and antimicrobial proteins released by activated neutrophils. Initially described as a means for neutrophils . We summarize how NETs are formed in response to various stimuli and provide evidence that NETosis is not universally a cell death pathway. Here we describe . 20 Altmetric. Metrics. Abstract. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) are chromatin structures loaded with antimicrobial molecules. They can trap and kill various . NETs are web‐like structures composed of fibers, DNA, histones, and various neutrophil granule proteins. NETs can capture and kill pathogens, including .
NETs are weblike DNA structures decorated with histones and antimicrobial proteins released by activated neutrophils. Initially described as a means for neutrophils .

1.2. NETosis Is a Double-Edged Sword. The seminal work of Brinkmann and colleagues (2004) first reported the ability of activated neutrophils to release nuclear DNA into the extracellular environment, where it can trap and neutralize pathogens in a process termed NETosis. The ability of various pathogens to induce NETosis (Abi Abdallah et . While knowledge regarding the (patho)physiological roles of NETosis is accumulating, little is known about the cellular and biophysical bases of this process. In this review, we describe and discuss our current knowledge of the molecular, cellular, and biophysical mechanisms mediating NET release as well as open questions in the field. NETosis is a cell death pathway whose principal consequence is ET formation. These ETs are important in order to control extracellular infections and constitute a way to concentrate the microbicide armamentarium limiting collateral tissue damage.
Neutrophils are critical to innate immunity, including host defense against bacterial and fungal infections. They achieve their host defense role by phagocytosing pathogens, secreting their granules full of cytotoxic enzymes, or expelling neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) during the process of NETosis. NETs are weblike DNA structures decorated . NETosis is a unique form of programmed cell death that neutrophils undergo when exposed to certain agents such as phorbol myristate acetate (PMA), bacterial LPS, Staphylococcus aureus (RN4220), or . NETosis usually needs the stimulation of neutrophils and the generation of ROS by NADPH oxidase (29, 35, 36). NETs generated from mitochondrial DNA are described ( 37 ) being the amount of mtDNA 100,000 times smaller than nuclear DNA because mitochondria are very few in neutrophils, but whether this difference plays any .NETosis is a unique form of cell death that is characterized by the release of decondensed chromatin and granular contents to the extracellular space. The initial observation of NETosis placed the process within the context of the innate immune response to infections. Neutrophils, the most numerous leukocytes that arrive quickly at the site of an infection, . Herein, we describe NETosis in different diseases focusing on the detrimental effect of NETs and outline possible therapeutics that can be used to mitigate netosis. There is a need for more studies and clinical trials on these and other compounds that could prevent or destroy NETs, thereby decreasing damage to patients.
Thus, CLR-mediated NETosis pathways are potent endogenous danger signals, and blocking C-type lectins may be a promising strategy to inhibit virus-induced NETosis and cytokine storm. Another CLR, Mincle, can mediate NET formation via modulation of autophagy without being affected by ROS, which is a major discovery in . NETosis has also been described in the pathophysiology of viral infections other than COVID-19. In normal conditions, NETosis is a regulated form of neutrophil death, which participates in the host’s immune defenses by the formation of traps to prevent the pathogen from spreading in the organism.
近年来,研究人员阐明了特定的受调节分子机制,受调节的细胞坏死的通路包括坏死性凋亡,焦亡、铁死亡和 NETosis。. 坏死性凋亡. 触发因素及特征: 坏死性凋亡(Necroptosis)是当细胞凋亡受阻时, .
Kubes and Fassl discuss the role of NETosis in sterile inflammation and disease, and propose windows of opportunity for therapeutic targeting of NETs. The production of neutrophil extracellular .
NETosis is activated not only by pathogens and their components, but also by platelets activated with either LPS or the plasma of septic patients also trigger NETosis. 36 Anti-neutrophil antibodies that can directly induce NETosis have also been isolated from patients suffering from the auto-immune disease small vessel vasculitis .netosisA role for NETosis in organ damage in lupus has been suggested by the detection of NETs in affected skin and kidney tissues in lupus patients. 24 NETosis can also induce vascular endothelial damage and clotting, suggesting that neutrophils might play a role in accelerated atherosclerosis and vascular complications in lupus patients. 24–26 .
NETosis appears to be tightly regulated and dysregulation has been implicated in severe autoimmune and autoinflammatory disease. Below, we discuss the molecular mechanisms that lead to release of NETs, taking into consideration the differences between different physiological stimuli in infection and highlighting the . NETosis is accepted as a specific form of cell death subroutine performed by granulocytes, differing from apoptosis and necrosis (1, 2). When neutrophils undergo NETosis, nuclear and granular membranes disintegrate, the chromatin decondenses, and it diffuses into the cytoplasm, mixing with cytoplasmic proteins.
Activated neutrophils release neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in response to a variety of stimuli. NETosis is driven by protein-arginine deiminase type 4, with the release of intracellular granule components that function by capturing and destroying microbes, including viral, fungal, bacterial, and protozoal pathogens. The .
netosis cell death Neutrophilic granulocytes release their own DNA (NETosis) as neutrophil extracellular traps to capture pathogens. Here, the authors use time-resolved fluorescence and atomic force microscopy and .
web4 de nov. de 2023 · O resultado do sorteio da +Milionária (concurso 92), de hoje, 4 de novembro, será divulgado no Espaço da Sorte, localizado em São Paulo. O prêmio estimado é de R$ 91 milhões. Foto: Reprodução. Números: 45 – 05 – 33 – 20 – 49 – 08. Trevos: 3 – 4.
netosis|netosis cell death